Assistant Professor In Electronics And Communication Kerala PSC 2022: Exam Made Easy

When it comes to opportunities for Electronics and Communication graduates, there is a lot to choose from. System Control Engineer, Electronics Engineer, Electronics Design and Development Engineer, Desktop Support Engineer, … The list goes on. Another option available is to qualify for the Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communication Kerala PSC exam.
Teaching is one of the most rewarding professions, and while assistant professor jobs in electronics and communication engineering are available in private colleges, it is always desirable to strive for a government job. This is because a government job would provide you with the stability and security you need.
Let’s take a look at what this post entails and how you can secure this job by honing your knowledge in our academy.
Basic Information about Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communication Kerala PSC
-
Name of the Post – Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communications Engineering
-
Department – Technical Education (Engineering Colleges)
-
Salary – AICTE Scale
-
Probation Period – 2 years
Qualification for Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communication Engineering
-
Educational Qualification – B.E/B.Tech and M.E/M.Tech in Electronics and Communication with first class or equivalent marks.
-
Age Limit – 20 – 39 (SC/ST candidates would be provided with relaxation)
A candidate must fulfil the above conditions to appear for the Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communications Kerala PSC 2022 exam.
-
Weightage Marks – Weightage marks are awarded for non-qualifying degrees (Additional qualifications apart from the basic educational qualification that makes you eligible for the post). For example, M.Phil, PhD, and Post Doctoral fellowships.
-
Last Appointment Details:-
- DOE – 27-02-2019
- Total Advice – 72
- Date of Last Advice – 24-02-2022
Assistant Professor ECE Exam Pattern
Kerala PSC selects candidates for Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communication through a written exam of 100 marks. This concludes the first phase of the exam. The second phase is an interview where the professional knowledge of the candidates is tested. Only those who secured above the cut-off marks will be called for the interview.
Once both the phases are over, a rank list is published from which the candidates will be chosen according to the available vacancy for Assistant Professor in electronics and communication.
The Assistant Professor in Electronics and Communication Kerala PSC Syllabus for the written exam is as follows;
- Module 1 – Mathematics (Engineering), Basic Civil Engineering, Basic Mechanical Engineering
- Module 2 – Basic Electrical Engineering, Basic Electronics Engineering, Basic Computer Science
- Module 3 – Networks and Devices
- Module 4 – Analog and Digital Circuits
- Module 5 – Signals and Systems
- Module 6 – Electromagnetics and Control Systems
- Module 7 – Communication and Instrumentation
assistant professor in electronics and communication kerala psc Detailed syllabus
Module I:
a) MATHEMATICS (ENGINEERING)
Matrices: Rank, systems of linear equations, consistency, Eigen values, Eigen vectors, Cayley Hamilton Theorem, diagonalization, linear dependence, and independence of vectors.
Partial Differentiation: Partial derivatives, Euler’s theorem on homogeneous functions, total derivatives, Jacobians, Taylor’s series (one and two variables) – Maxima and minima of functions of two variables – Lagrange’s method.
Vector Differentiation: Scalar and vector functions, differentiation of vector functions – velocity and acceleration – scalar and vector fields – operator – Gradient – Directional derivative – Divergence – Curl – irrotational and solenoidal fields – scalar potential.
Laplace Transforms: Transforms of elementary functions, shifting property – inverse transforms – transforms of derivatives and integrals – transform of functions multiplied by t and divided by t – convolution theorem, solution of ordinary differential equations with constant coefficients using Laplace transforms.
Ordinary Differential Equations: First Order ordinary differential equations, systems of linear first-order ordinary differential equations, linear ordinary differential equations of higher order with constant coefficients, linear second-order ordinary differential equations with variable coefficients (Cauchy and Legendre equations), Method of Laplace transforms for solving ordinary differential equations.
Complex Analysis: Analytic functions, conformal mappings, bilinear transformations, complex integration, Cauchy’s integral theorem and formula, Taylor and Laurent’s series, residue theorem. Fourier Series: Fourier series of periodic functions of period 2 π and 2 ℓ, odd and even functions, Half range expansions.
b) BASIC CIVIL ENGINEERING
Mechanics – statistics – Coplanar forces – conditions of equilibrium. Support reactions – Simply supported and overhanging beams. Friction – Laws of friction – applications. Centre of gravity and moment of inertia of plane areas. Dynamics – rectilinear motion – Newton’s laws of motion – curvilinear motion.
Building materials – common building materials – stone, brick, cement, steel, aggregate, concrete, timber – properties, IS specification. Building construction – types and functions of the following structural components of buildings – foundations and superstructure.
Surveying – the principle of surveying – linear measurements using chain – levelling work – reduction of levels.
c) BASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Zeroth, first and second laws of thermodynamics, CI and SI Engines, properties of steam. Centrifugal and reciprocating pumps, hydraulic turbines, refrigeration and air conditioning, hydro-electric, thermal, and nuclear power plants, mechanical power transmission systems such as belt, rope, chain and gear, manufacturing process – casting, forging, rolling, brazing, soldering, and welding, machining process – turning, shaping, drilling, grinding and milling. Conic sections and miscellaneous curves, orthographic, isometric, and perspective projections.
Module II:
a) BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
-
Ohm’s law, Kirchoff’s laws – solution of series and parallel circuits with dc excitation.
-
Magnetic circuits: MMF, field strength, flux density, reluctance, electromagnetic induction, Faraday’s laws, Lenz’s law, statically and dynamically induced EMFs, self and mutual induction, co-efficient of coupling.
-
Principle of generation of alternating current – waveforms – frequency, period, average and RMS values, form factor.
-
Generation of 3 phase ac voltage, star and delta connections, voltage & current relationships in star and delta (balanced system only).
-
Principle of operation of dc motor & generator, single phase transformer, and three phase induction motor.
-
Types of lamps, the necessity of earthing.
b) BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
-
Devices – working principle of PN junction, Zener diode, and BJT.
-
Systems – Rectifiers: Half wave, Full wave, and Bridge. Filters: Capacitors and Inductors.
-
Amplifiers & Oscillators – Common Emitter RC coupled amplifier and its frequency response. Principles of Wein-bridge oscillator. Op-amps: Basics, inverting, and non-inverting amplifier.
-
Communication – Need for modulation, principles of AM and FM.
-
Measurements – Working principles of CRO and Multimeter.
c) BASIC COMPUTER SCIENCE
-
Functional units of a computer.
-
Programming in C – control structures, functions.
Module III: Networks and Devices
Network theorems: superposition, Thevenin and Norton’s maximum power transfer, time domain analysis of simple RC, RL, and RLC circuits, solution of network equations using Laplace transform: frequency domain analysis of RL, RC, and RLC circuits, 2-port network parameters: driving point and transfer functions.
Electronic Devices: Energy bands in silicon, carrier transport in silicon, diffusion current, drift current, mobility and resistivity, generation and recombination of carriers, working principles of p-n junction diode, Zener diode, tunnel diode, BJT, JFET, MOSFET, LED and photodiode.
Module IV: Analog and Digital Circuits
Simple diode circuits: clipping & clamping, biasing and bias stability of BJTs and MOSFETs, small signal equivalent circuits of BJTs and MOSFETs. Amplifiers: single stage, differential, feedback, and power. Frequency response of amplifiers. Op-amp circuits: Inverting, non-inverting, Integrator, and Comparator. Sinusoidal Oscillators: criterion for oscillation, single transistor, and op-amp configurations.
Boolean algebra, minimization of Boolean functions, logic gates, combinational Circuits: arithmetic circuits, code converters, multiplexers and decoders, sequential circuits: latches and flip-flops, counters, and shift registers, ADCs and DACs, microprocessor (8085): architecture and programming.
Module V: Signals and Systems
Introduction to signals and systems, Linear Time-invariant (LTI systems): definitions and properties, causality, stability, impulse response and convolution, continuous-time and discrete-time Fourier series, continuous-time and discrete-time Fourier Transform Z-transform: definition, properties, and inverse, stability analysis using pole-zero plot, difference equation solution using unilateral Z-transform, DFT and its properties, FFT: radix 2 and composite radix algorithm, sampling theorem, the realization of IIR and FIR structures – parallel and cascade structure, frequency response, group delay and phase delay, signal transmission through LTI systems.
Module VI: Electromagnetics and Control Systems
Elements of vector calculus: divergence and curl, Gauss and Stokes theorems, Maxwell’s equations, differential, and integral forms, wave equation, Poynting vector, Plane waves: propagation through various media, reflection and refraction, phase and group velocity and skin depth, Transmission lines: characteristic impedance, impedance transformation. Waveguides: modes in rectangular waveguides, boundary conditions, cut-off frequencies, and dispersion relations, basics of propagation in dielectric waveguide and optical fibers, basics of Antennas: Dipole antennas, radiation pattern, antenna gain.
Introduction to control systems, signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems, transient and steady-state analysis of LTI control systems and frequency response, tools and techniques for LTI control system analysis: root loci, Routh-Hurwitz criterion, Bode and Nyquist plots.
Module VII: Communication and Instrumentation
Analog communication systems: amplitude and angle modulation and demodulation systems, superheterodyne receivers, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Digital communication systems: pulse code modulation (PCM), differential pulse code modulation (DPCM), digital modulation schemes: amplitude, phase, and frequency shift keying schemes, matched filter receivers, fundamentals of information theory and channel capacity theorem, random signals and noise: probability, random variables, probability density function, autocorrelation, power spectral density.
Static and dynamic characteristics of Measurement systems: Measurement of displacement, velocity and acceleration, force, basics of fiber optics, biomedical instruments, EEG, ECG and EMG, Clinical measurements, ultrasonic transducers.
assistant professor ECE Previous Year Question Paper Analysis
assistant professor in electronics and communication kerala psc coaching
Earnest Academy provides affordable online coaching classes to help you fulfil your goals. We provide online coaching for a variety of technical Kerala PSC exams.
The online coaching for Assistant Professor Electronics and Communication, like all our other courses, is handled by our team of experienced faculty. Our online coaching also provides flexibility in timings to ensure that those who are working can also enrol with us.
Our Assistant Professor in electronics and communications Kerala PSC coaching classes are structured in such a way as to cover everything from the basics to the core of each subject.
We, at Earnest Academy, believe in the importance of practice and therefore make sure to include previous question papers in our discussions. We also provide regular quizzes and assignments which are evaluated to check the progress of the students.
Features of our Online Coaching Class
Subject-specific classes to ensure the efficient coverage of relevant portions.
Classes that are planned around previous year questions to ensure your success.
Quizzes, assignments, and online mock tests to build accountability.
Flexible timings to include working professionals.
Mentor Support.
High-quality study materials are prepared and compiled by our in-house experts.
Doubt clearance and interactive sessions with our subject matter experts.
A coordinator is assigned to each batch to collect queries and feedback and give individual attention to each student.
kerala psc assistant professor electronics and communication study materials (Oned app)
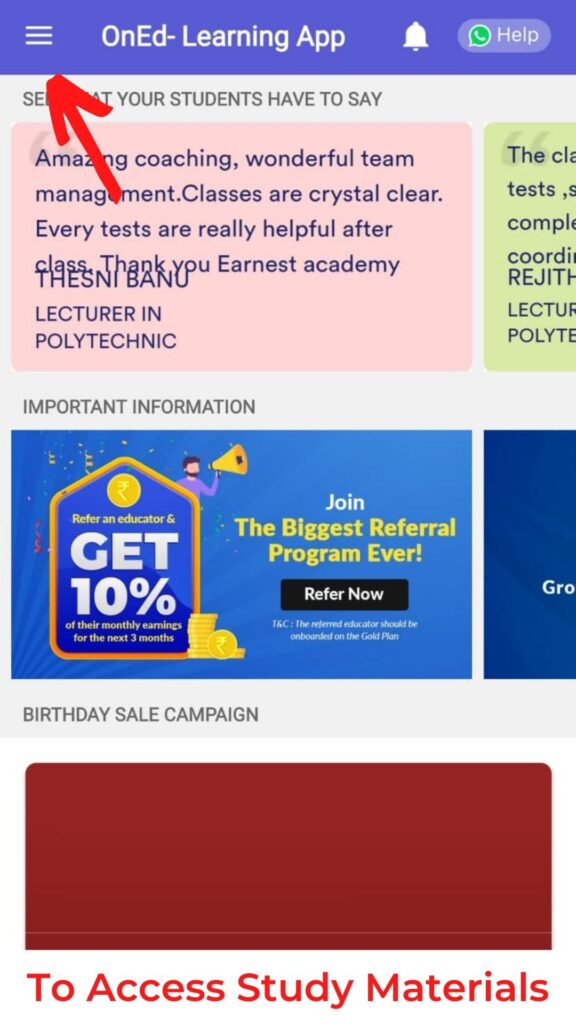
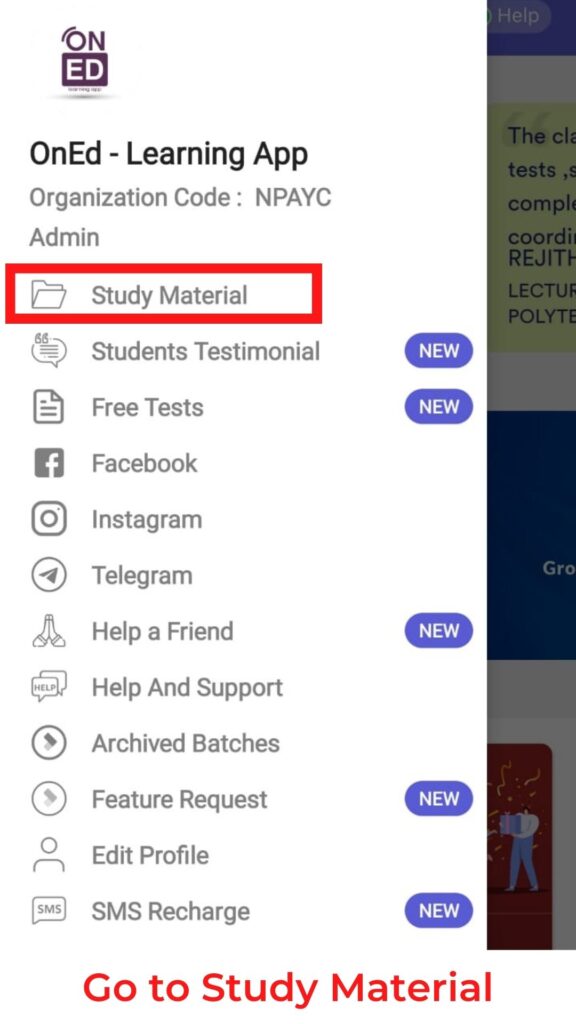
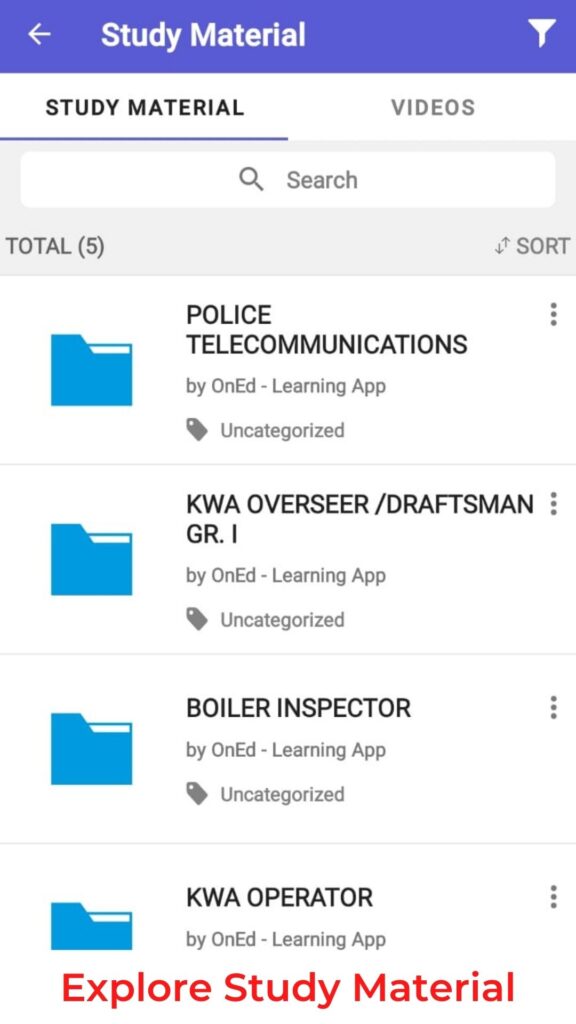
We provide our own specialized study materials to ensure that our students work smart instead of working hard. Our in-house experts have created these study materials with the aim of providing a one-stop destination for all our students’ needs. You can access study materials, and demo classes related to Assistant Professor electronics communication Kerala PSC from our learning app.
Our Mentors
Why Choose Earnest Academy?
Each year Kerala PSC witnesses an ever-increasing number of candidates competing for various government posts. The demand for government posts and the resulting competition for them increases with each passing year. Working hard is no longer the solution, the solution is to work smart.
Earnest Academy was established on 2019 with that vision. We provide specialized study materials, mentor support, and live classes handled by our team of IITians and NITians to ensure that our students work smart towards their goals. Our coaching classes for Assistant Professor In Electronics And Communication Kerala PSC are tailored to meet the latest question pattern and curricula.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the age limit for the govt jobs for Assistant Professor in electronics and communication?
The age limit is 20 to 39.
Do you provide offline downloads?
Yes, if you use our app you can use the offline download feature.
Are the tests part of the online course?
We provide regular tests and quizzes to provide you with the practice you need to ace this exam.
Do I need a Ph.D. to apply for the Assistant Professor Kerala PSC?
No, as per the norms, Ph.D. is not mandatory to apply for this post.
I have lost touch with the core subjects, can I still clear Assistant Professor In Electronics and Communication Kerala PSC?
Of course. Our courses are impeccably structured and we make sure to cover all the basics in great depth to ensure conceptual understanding.

